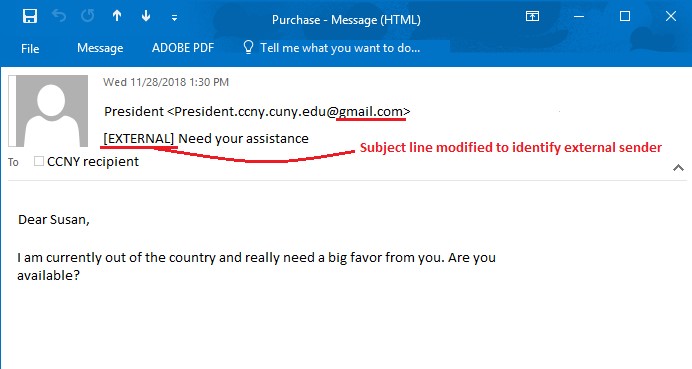
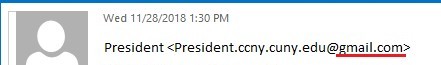
Organization email is used to convey information externally (to customers/clients) and internally (to staff within the company). The [External] tag does not mean the message is a scam, but it does provide additional information about the message source. The [External] tag is there to help. The [External] tag means you need to stop and think about this email.
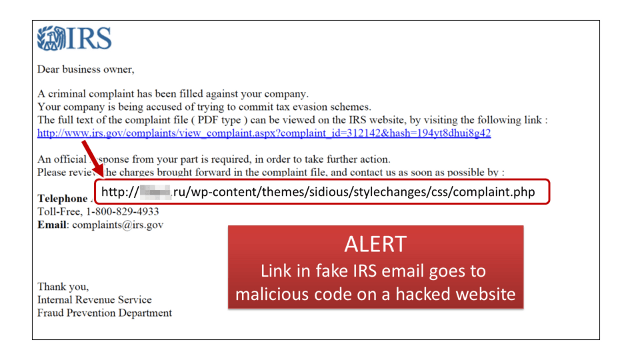
Sometimes a link masks the website to which it links. If you hover over a link without clicking it, you’ll notice the full URL of the link’s destination in a lower corner of your browser. Link scanners allow you to enter the URL of a suspicious link and check it for safety.
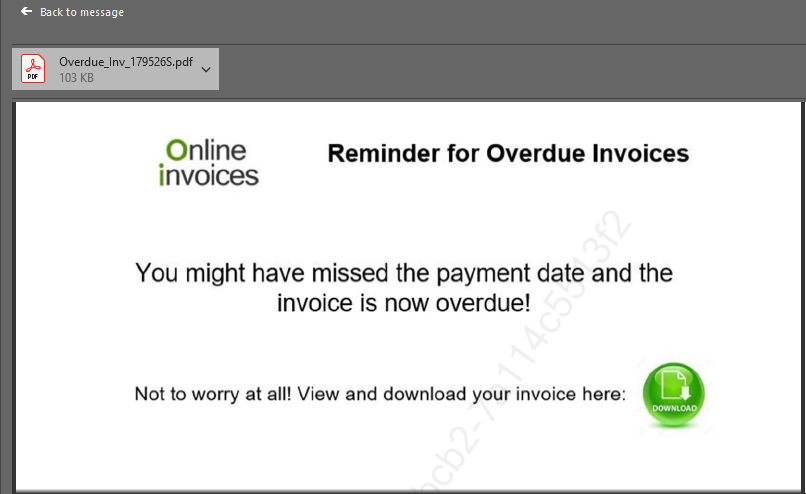
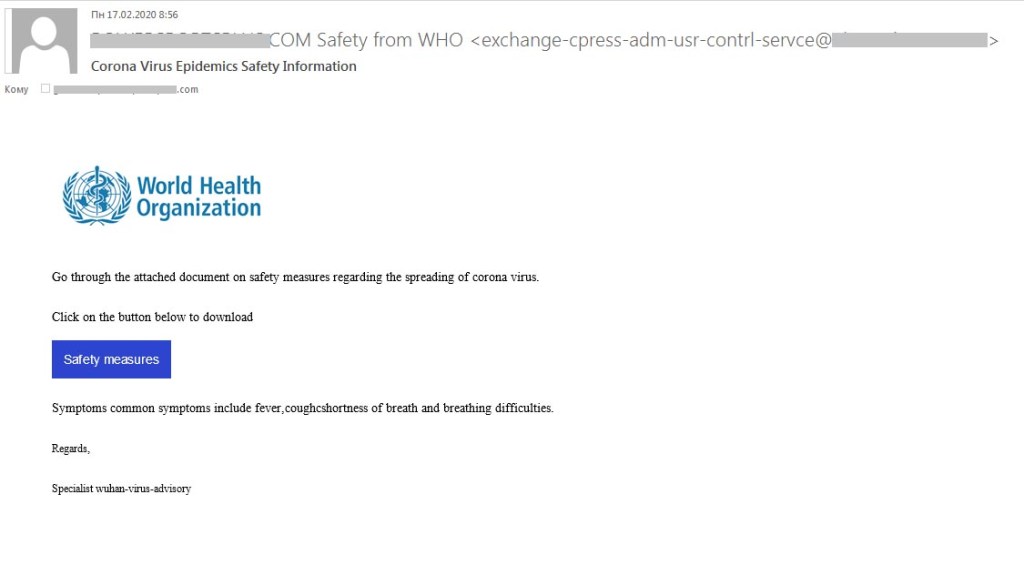
Attacker will use them to fool the user to downloading malware or to other ends, which can often include invoice fraud. While the email itself might seem to be harmless, often downloading the attachment alone can be enough to unleash the malware and do extensive damage. Disguised as documents, voicemails, e-faxes or PDFs, malicious email attachments are designed to launch an attack on the victim's computer when the attachment is opened.
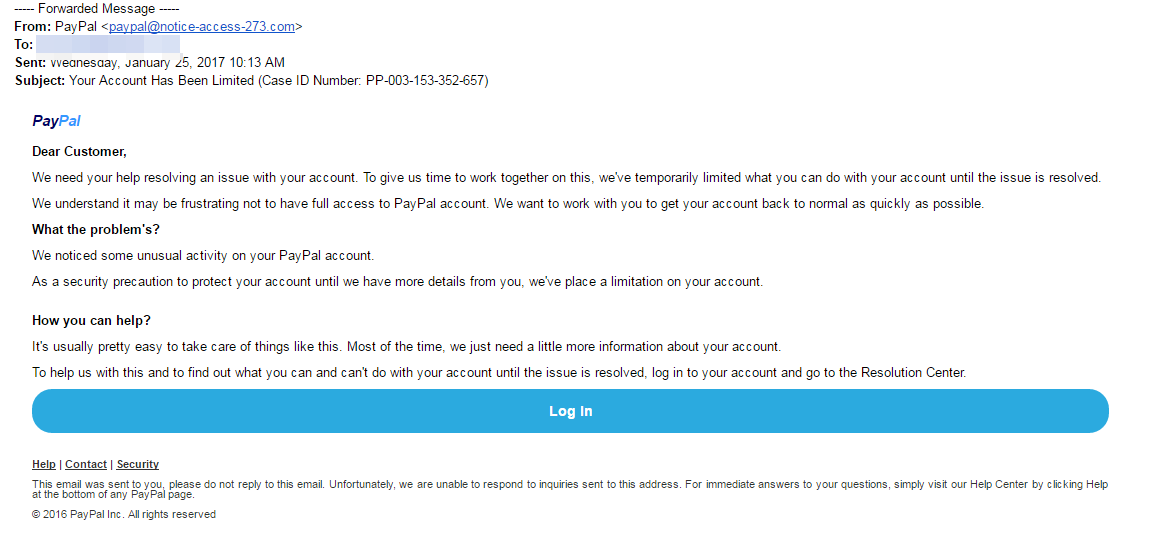
Fake emails, also known as 'phishing' or 'spoof' emails, attempt to trick you into revealing personal or financial information such as bank account details, credit card details and passwords. Example: Even if a URL contains the word 'PayPal', it may not be a PayPal webpage.
Email spoofing is the creation of email messages with a forged sender address for the purpose of fooling the recipient into providing money or sensitive information. The message uses your company’s letterhead, looks as legitimate as the 401k notices you’ve received before and has a login link or University semester fee payment reminder. Cyber-criminal craft it to adapt in to victims environment.